Double Prompt Learners: Classifier and Discriminator Mechanisms for Noisy Label Learning
研究背景
预训练-微调范式 (Pre-Training and Fine-Tuning(PT-FT)) 已经成为自然语言处理和多模态领域中的主流,针对视觉语言模型,通过提示学习微调预训练模型适配下游数据集已经被广泛地证明有非常好的泛化性能。然而对于大量各异的下游任务场景 (图像分类、识别、分割等任务),精细地筛选数据集以及采用大量样本学习将会是模型迁移应用的局限之处,因此我们旨在探索一种**借助少样本学习适应下游噪声数据集并且能够通过不断学习增强模型性能的鲁棒性提示学习机制**,甚至可以应用到通过模型与环境不断的交互作用,既不用采集大量样本学习,也无需精细挑选数据集,这对模型泛化和迁移性能提供了极大便利。
研究领域
- Noisy Label Learning
- Few-shots Learning
- Prompt Learning
- Visual Language Models(VLMs)
研究基础
- 数据:下游任务数据集存在噪声(标注错误);
- 模型:Visual Language Models (VLMs);
- 目标:在有噪音的下游任务上学习一个 Robust 的模型;
- 方式:fine-tune pre-trained model,few-shots learning;
相关工作
PTNL, Robust To Noisy Labels
Visual-Language Models
Findings
- 固定的类 Tokens 对模型优化能够提供强有力的约束作用;
- 提示学习能够抑制噪声样本的梯度更新;
- 预训练的图像文本嵌入为图像分类提供了强有力的先验知识;
Conclusions
- CLIP 本身具有一定的噪声鲁棒性;
- CLIP 对下游任务具有强有力的先验知识;
VLM-CPL, Vision-Language Models-Consensus Pseudo Labels
Framework
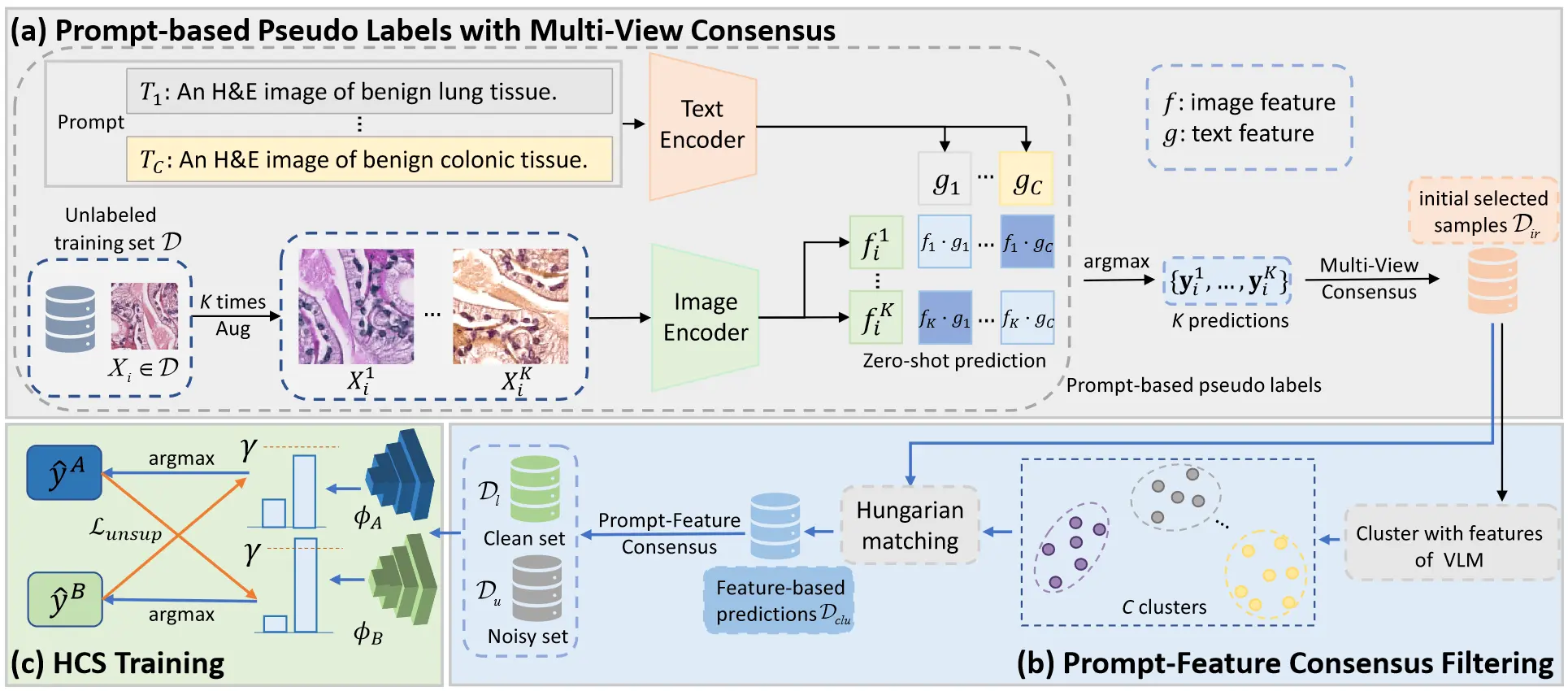
- 利用VLM的零样本推理获得基于提示的伪标签;
- 在特征空间中对样本进行聚类获得基于特征的伪标签;
- 构造提示-特征共识伪标签划分噪声数据集进行训练;
Strength
- 通过数据增强获取单个样本的多个预测标签;
- 引入标签共识增强噪声样本划分的置信度;
Problems
- 数据增强不会解决预训练模型对某些类别的偏好作用;
- 数据增强的样本数以及可信样本过滤的比例需要手动设置;
- Hungarian Matching 会引入额外的误差,使得伪标签不够准确;
激励分析
- 如何构造多个决策体,使得集成决策的策略能够缓解或避免单个模型的偏好作用;
- 如何利用 VLMs 的预训练知识筛选噪声样本以及伪标签增强;
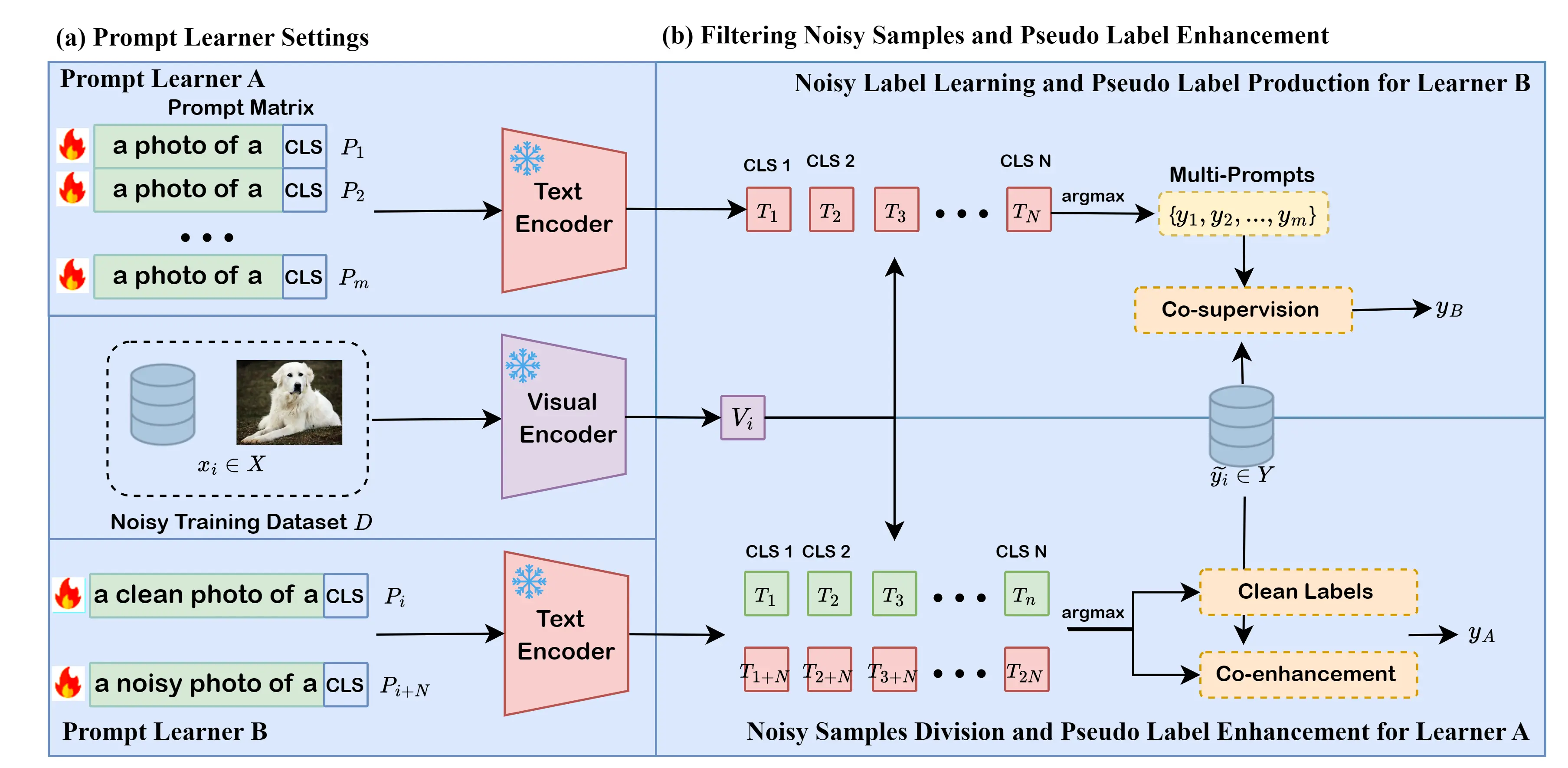
Double Prompt Learners
CLIP 利用类别提示特征与图像特征之间的余弦相似度进行分类,最大的潜力在于 CLIP 预训练在通用大规模数据集上,能够表现出较好的泛化性能,由于其庞大的学习参数以及多样的通用知识,CLIP 被证明本身便具有一定的噪声鲁棒性。我们设想扩展 CLIP 的文本提示空间以能够引导对噪声样本和干净样本的筛选,即基于CLIP构建分类器与判别器,通过相互学习来不断增强模型性能。
CLIP 分类器
根据之前的探究,我们发现对每个类别设定多个提示词能够进一步缓解由于上下游数据集领域不同带来的偏差作用,典型的有类别偏置。这种提示集成策略有利于对样本分类提供更加可信的特征相似度,对样本噪声的鲁棒性也会更强。
Prompts 设置
- 对每一个 class 设置多个提示词,即
- PT1: [< a photo of > < class >]
- PT2: [< a photo of > < class >]
- …
- PTm: [< a photo of > < class >]
CLIP 判别器
Prompts 设置
- 对每一个 class 设置噪声样本提示与干净样本提示,即
- [< a clean photo of > < class >]
- [< a noisy photo of > < class >]
Framework
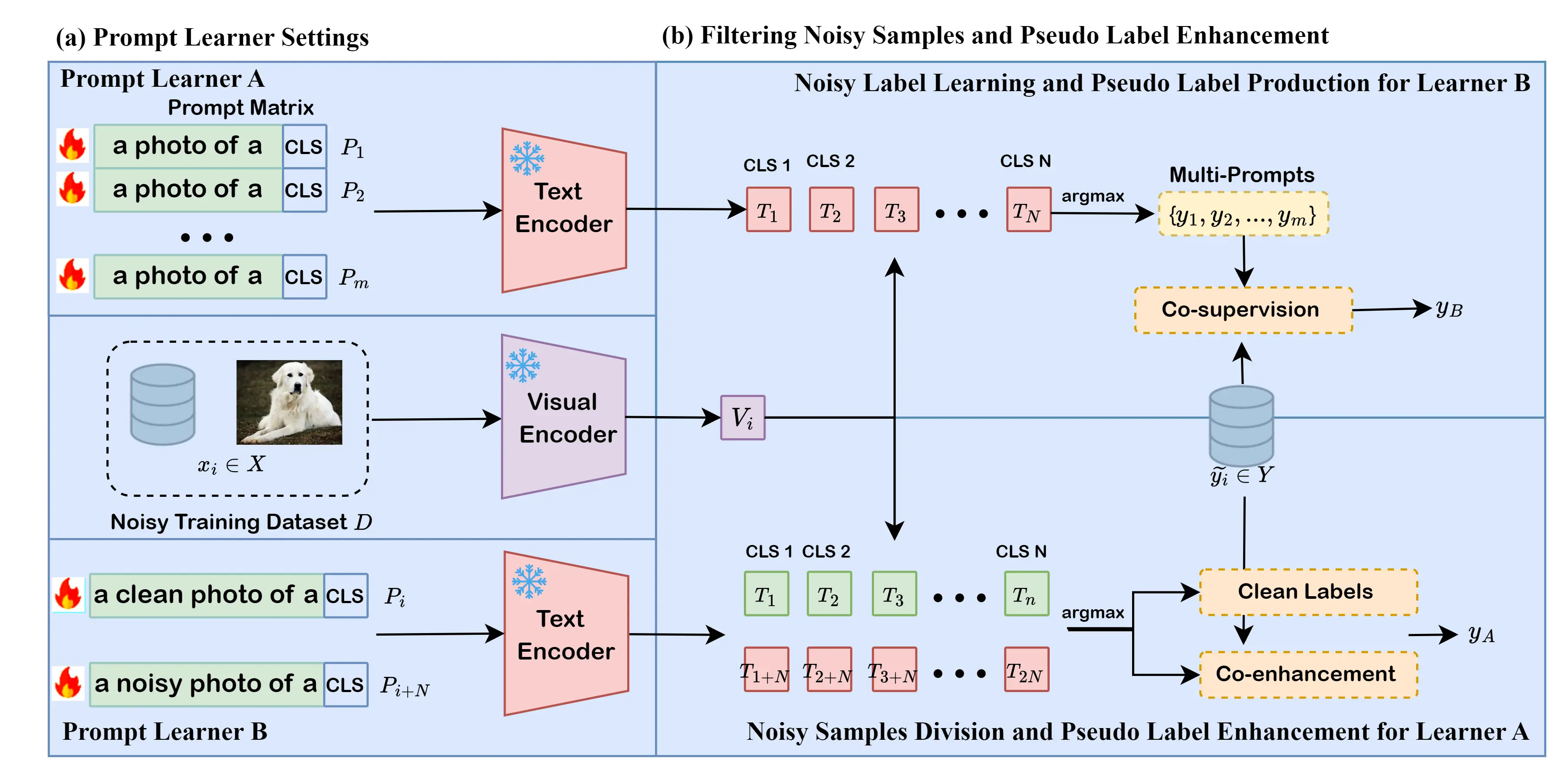
特点分析
- 模型的作用
- Prompt Learner A 用于下游任务的分类预测,分类器;
- Prompt Learner B 用于噪声样本筛选以及标签更正,判别器;
- 模型学习动力
- 前提是 A 有一定可信度的预测能力,预训练的 CLIP 足以满足;
- 通过 A 的预测标签对比原有标签,对 B 提供筛选标签;
- B 筛选样本后获得的标签更新 A;
- Learner A 与 Learner B 相互增强
- Learner A 学习能力增强,使得分类更准确,提供给 B 的监督作用越强;
- Leaner B 筛选噪声样本能力更强,提供给 A 的标签就更准确;
Experiments
Requirements
To accelerate training double prompt learners and abalation experinments, we used two GPUs: RTX 2080-Ti and construct the shell codes template for running only once.
- Screen 0
1 | screen -S cuda0 |
- Screen 1
1 | screen -S cuda1 |
Shell Codes
We configure all experiments in a shell script so that it’s very convenient to conduct Validation Experiments and Ablation Experiment. After running experiments, the script immediately did result analysis.
1 |
|
Results
Abalation Study for DPL – prompt blocks $m$
- dataset: Dtd
- noise rate: 0 | 12.5% | 25% | 50%
- backbone: Text: ViT-B/32-PT, Visual: RN50-PT
- weight parameter $\beta$: 0.5
| Prompt Blocks$m$ | Noise Rate | Noise Rate | Noise Rate | Noise Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 12.5% | 25% | 50% | |
| PTNL | 62.86% | 58.90% | 53.62% | 46.19% |
| 1 | 63.10% +- 0.83% | 61.58% +- 0.25% | 60.40% +- 1.40% | 53.65% +- 0.47% |
| 2 | 63.26% +- 0.60% | 60.78% +- 0.56% | 60.62% +- 0.89% | 54.59% +- 1.28% |
| 4 | 63.51% +- 0.94% | 61.37% +- 0.71% | 59.97% +- 0.88% | 54.73% +- 0.89% |
| 6 | 63.06% +- 0.41% | 60.93% +- 0.66% | 59.91% +- 1.06% | 54.43% +- 1.90% |
- dataset: Caltech101
- noise rate: 0 | 12.5% | 25% | 50%
- backbone: Text: ViT-B/32-PT, Visual: RN50-PT
- weight parameter $\beta$: 0.5
| Prompt Blocks$m$ | Noise Rate | Noise Rate | Noise Rate | Noise Rate | MeanAcc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 12.5% | 25% | 50% | ||
| PTNL | 90.65% | 82.51% | 78.70% | 70.13% | 80.50% |
| 1 | 91.33% +- 0.29% | 90.48% +- 0.57% | 88.93% +- 0.17% | 85.37% +- 1.87% | 89.03% |
| 2 | 91.37% +- 0.17% | 90.82% +- 0.17% | 89.36% +- 0.47% | 84.12% +- 2.33% | 88.92% |
| 4 | 91.25% +- 0.65% | 90.68% +- 0.14% | 89.16% +- 0.04% | 84.41% +- 2.72% | 88.88% |
Abalation Study for DPL – weight parameter $\beta$
- dataset: Dtd
- noise rate: 0 | 12.5% | 25% | 50%
- backbone: Text: ViT-B/32-PT, Visual: RN50-PT
- prompt blocks $m$: 4
| $\beta$ | Noise Rate | Noise Rate | Noise Rate | Noise Rate | MeanAcc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 12.5% | 25% | 50% | ||
| PTNL | 62.86% | 58.90% | 53.62% | 46.19% | 55.39% |
| 0.0 | 62.37% +- 0.36% | 61.21% +- 0.49% | 59.44% +- 2.08% | 53.65% +- 0.98% | 59.17% |
| 0.1 | 62.51% +- 0.41% | 60.96% +- 0.91% | 59.99% +- 1.19% | 53.23% +- 0.93% | 59.17% |
| 0.2 | 63.02% +- 0.27% | 61.17% +- 0.97% | 60.87% +- 0.68% | 53.59% +- 2.33% | 59.66% |
| 0.3 | 62.67% +- 0.41% | 61.15% +- 0.93% | 59.83% +- 1.12% | 55.16% +- 1.40% | 59.70% |
| 0.4 | 63.59% +- 0.77% | 61.39% +- 0.85% | 60.13% +- 0.39% | 55.18% +- 2.15% | 60.07% |
| 0.5 | 63.51% +- 0.94% | 61.37% +- 0.71% | 59.97% +- 0.88% | 54.73% +- 0.89% | 59.89% |
| 0.6 | 62.37% +- 0.75% | 61.39% +- 0.98% | 59.89% +- 1.64% | 53.19% +- 1.94% | 59.21% |
| 0.7 | 62.86% +- 0.65% | 61.03% +- 0.77% | 59.95% +- 1.43% | 53.86% +- 0.27% | 59.43% |
| 0.8 | 62.96% +- 0.33% | 60.28% +- 0.90% | 59.93% +- 0.89% | 53.05% +- 3.58% | 59.06% |
| 0.9 | 62.49% +- 0.31% | 61.05% +- 0.33% | 59.48% +- 0.96% | 53.03% +- 1.61% | 59.01% |
| 1.0 | 63.10% +- 0.39% | 60.22% +- 0.48% | 59.18% +- 1.12% | 51.91% +- 2.52% | 58.60% |
- dataset: Caltech101
- noise rate: 0 | 12.5% | 25% | 50%
- backbone: Text: ViT-B/32-PT, Visual: RN50-PT
- prompt blocks $m$: 4
| $\beta$ | Noise Rate | Noise Rate | Noise Rate | Noise Rate | MeanAcc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 12.5% | 25% | 50% | ||
| PTNL | 90.65% | 82.51% | 78.70% | 70.13% | 80.50% |
| 0.0 | 90.90% +- 0.34% | 90.56% +- 0.29% | 90.17% +- 0.18% | 88.67% +- 0.25% | 90.07% |
| 0.1 | 91.02% +- 0.30% | 90.92% +- 0.11% | 90.29% +- 0.52% | 88.94% +- 0.61% | 90.29% |
| 0.2 | 90.90% +- 0.21% | 90.97% +- 0.28% | 90.24% +- 0.19% | 88.75% +- 0.73% | 90.21% |
| 0.3 | 91.04% +- 0.25% | 90.40% +- 0.15% | 90.01% +- 0.14% | 88.56% +- 0.67% | 90.00% |
| 0.4 | 91.00% +- 0.42% | 90.72% +- 0.18% | 89.93% +- 0.17% | 87.75% +- 0.90% | 89.85% |
| 0.5 | 91.25% +- 0.65% | 90.68% +- 0.14% | 89.16% +- 0.04% | 84.41% +- 2.72% | 88.88% |
| 0.6 | 91.07% +- 0.21% | 90.45% +- 0.30% | 88.63% +- 0.63% | 83.02% +- 2.72% | 88.29% |
| 0.7 | 90.86% +- 0.24% | 90.57% +- 0.30% | 88.69% +- 0.19% | 83.08% +- 3.39% | 88.30% |
| 0.8 | 91.14% +- 0.36% | 90.52% +- 0.29% | 89.55% +- 0.52% | 81.42% +- 1.66% | 88.16% |
| 0.9 | 90.98% +- 0.02% | 90.18% +- 0.59% | 88.92% +- 0.42% | 83.48% +- 1.10% | 88.39% |
| 1.0 | 91.25% +- 0.37% | 90.64% +- 0.30% | 89.24% +- 0.58% | 84.46% +- 0.75% | 88.90% |
Raw Materials
Model traning logs can be found in the log.txt under each experimental directory.
Parsing results can be found in the following files:
- Dataset: Dtd
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_1BLOCK_0.5BETA ON Dtd
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_2BLOCK_0.5BETA ON Dtd
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_4BLOCK_0.0BETA ON Dtd
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_4BLOCK_0.1BETA ON Dtd
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_4BLOCK_0.2BETA ON Dtd
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_4BLOCK_0.3BETA ON Dtd
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_4BLOCK_0.4BETA ON Dtd
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_4BLOCK_0.5BETA ON Dtd
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_4BLOCK_0.6BETA ON Dtd
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_4BLOCK_0.7BETA ON Dtd
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_4BLOCK_0.8BETA ON Dtd
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_4BLOCK_0.9BETA ON Dtd
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_4BLOCK_1.0BETA ON Dtd
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_6BLOCK_0.5BETA ON Dtd
- Dataset: Caltech101
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_1BLOCK_0.5BETA ON Caltech101
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_2BLOCK_0.5BETA ON Caltech101
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_4BLOCK_0.0BETA ON Caltech101
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_4BLOCK_0.1BETA ON Caltech101
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_4BLOCK_0.2BETA ON Caltech101
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_4BLOCK_0.3BETA ON Caltech101
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_4BLOCK_0.4BETA ON Caltech101
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_4BLOCK_0.5BETA ON Caltech101
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_4BLOCK_0.6BETA ON Caltech101
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_4BLOCK_0.7BETA ON Caltech101
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_4BLOCK_0.8BETA ON Caltech101
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_4BLOCK_0.9BETA ON Caltech101
- DPL RN50_EP50_16SHOTS_4BLOCK_1.0BETA ON Caltech101
References
Double Prompt Learners: Classifier and Discriminator Mechanisms for Noisy Label Learning